We have cacti and succulents from Madagascar, North and South America, and South Africa.
In addition, we have a bed with gymnosperms.
Madagascar
Madagascar is one of the most exciting places on Earth. There are no native cacti in Madagascar, but the flora is unique.
About 80% of Madagascar’s vascular plants are endemic, including several succulents.
Large succulent woodlands can be found in the semi-arid regions southwest on the island, where there is a dry season for 7-8 months of the year.
.jpeg)
North-America
You will find most cacti species in Mexico, but their overall distribution extends from Mexico to Canada.
They grow in the desert and in many other "semi-arid" areas such as coastal cliffs, dry steppe and shrublands, and low-growing tropical forests.
Cacti play an important role for many animal species in the arid landscape, especially the slightly larger cacti such as saguaro and candelabra. These species are an important source of food and water.
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
South-America
Cacti are found in large parts of South America, with the exception of the Amazon and in the far south of the continent. Brazil is the country with the highest species diversity.
In this exhibition we have focused on the cactus landscape seen in the Andes.
We divide these cacti into two ecological groups: Those which live in the high arid areas and those which live in the tropical forests at the foothills.
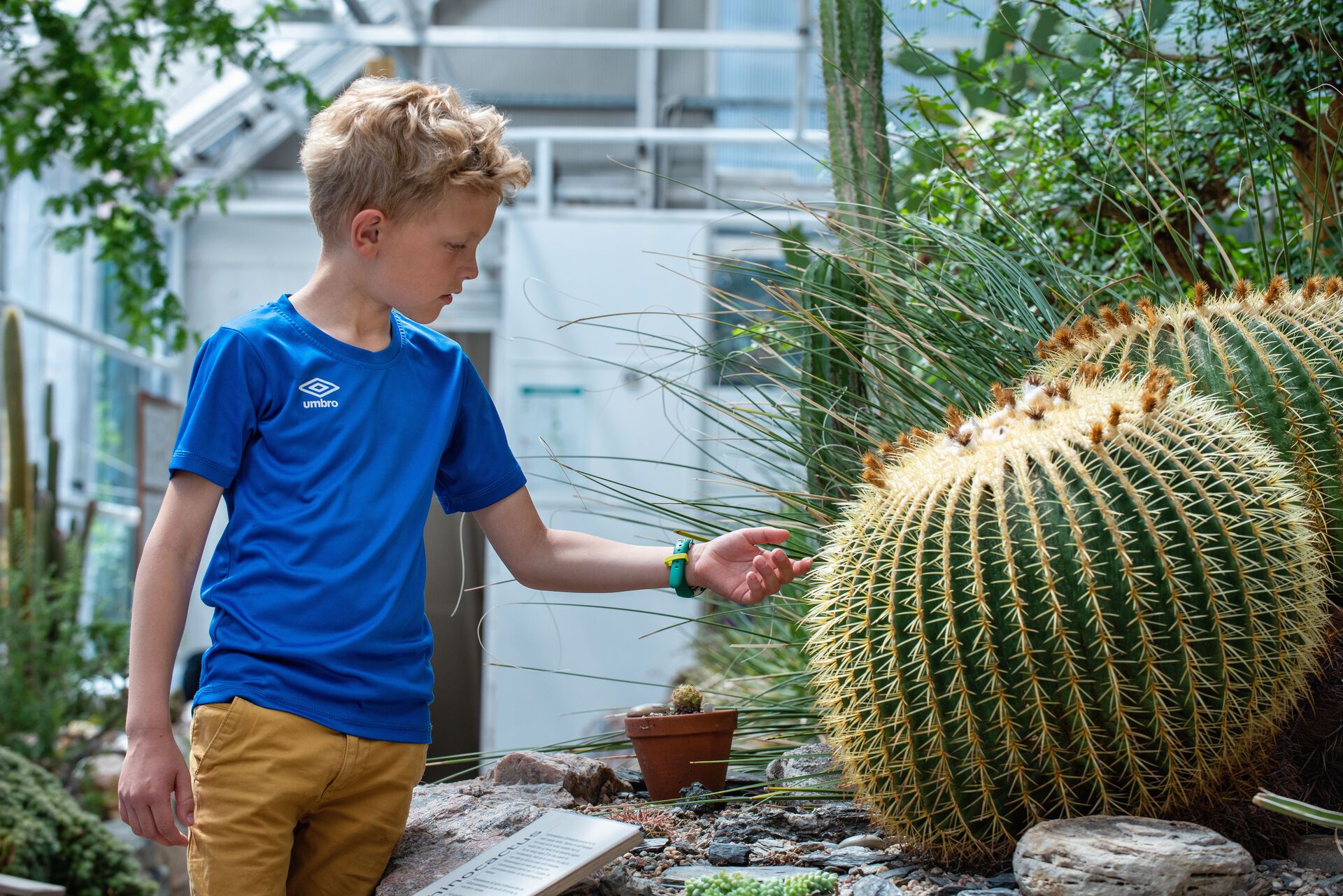

South-Africa
In the dry areas of South Africa’s and Namibia’s west coast there are no cacti but the largest diversity of succulents on earth.
One third of the world’s 10.000 succulents are located here, and several are endemic. The drought area is divided into a winter-rainfall and summer-rainfall zone.
The fog belt, resulting from warm air meeting the cold Atlantic Ocean currents, is an important source of humidity for life in the dry areas along the coast of Namibia.
Gymnosperms
Gymnosperms include conifers, cycads, ginkgo and gnetophytes. This is reflected in their name, «gymnos» meaning naked and «sperma» meaning seed.
Unlike flowering plants, their seeds are not surrounded by a fruit but are exposed on the surface of cone-like structures.
The gymnosperms emerged approximately 360 million years ago, making them the first seed-producing plants. However flowering plants dominate Earth today.
Conifers still constitute a significant and substantial part of the world’s forests, especially in the northern hemisphere.
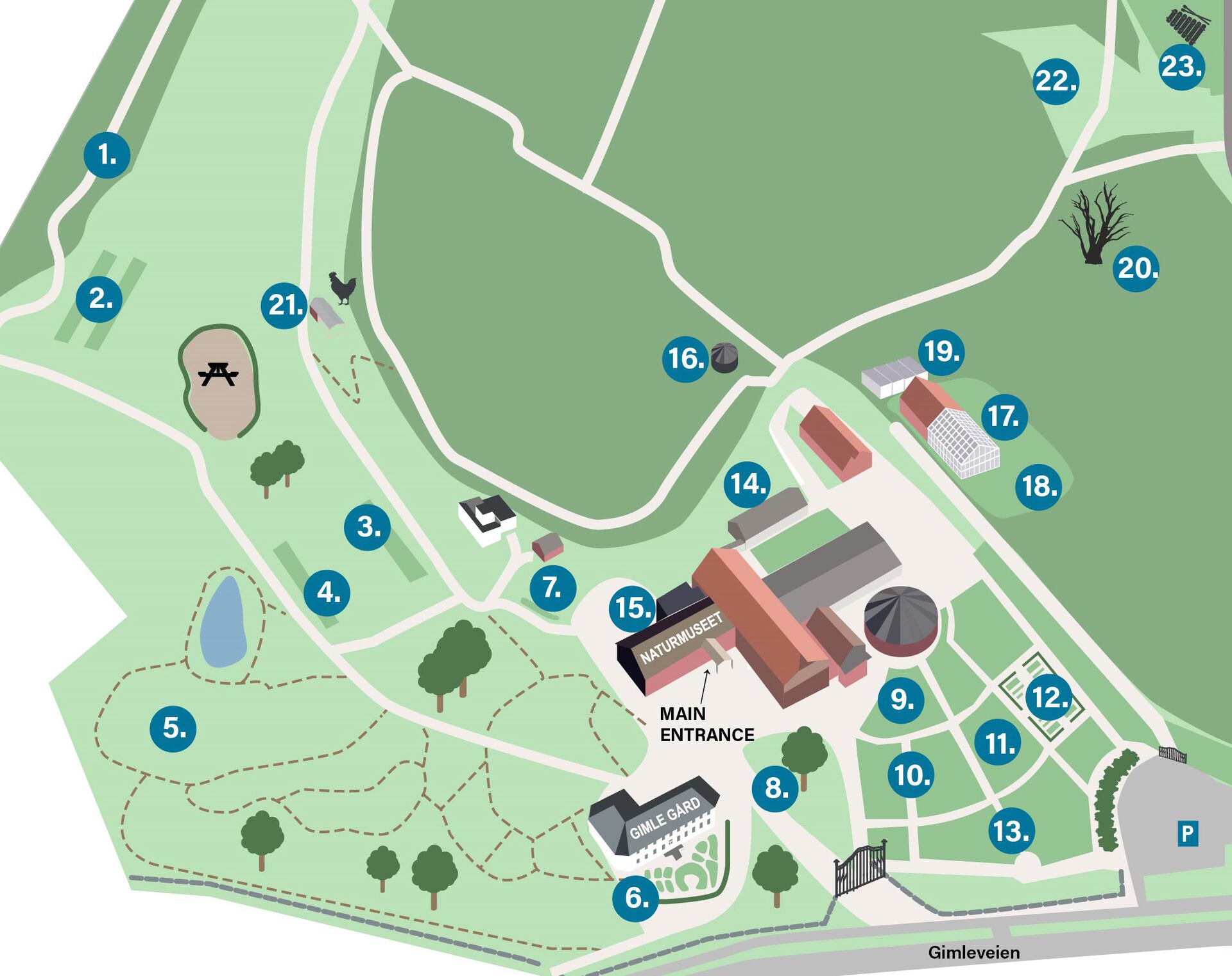
1. Conifers arboretum, 2. Dahlia, 3. Perennials, 4. Peonies, 5. Old park, 6. Historical Rose Garden, 7. Fern collection, 8. Roch exhibition, 9. Modern Roses, 10. Theme gardens, 11. Millennium Garden, 12. Monastery Garden, 13. Roses of Southern Norway, 14. Cacti House / Exhibition greenhouse, 15. café, 16. Cabin, 17. Glasshuset/Production Greenhouse, 18. Plant production grounds, 19. Office module, 20. Protected oak, 21. Chicken coop, 22. Wildflower meadow, 23. Music instruments
